Visualize the value generated by your organization
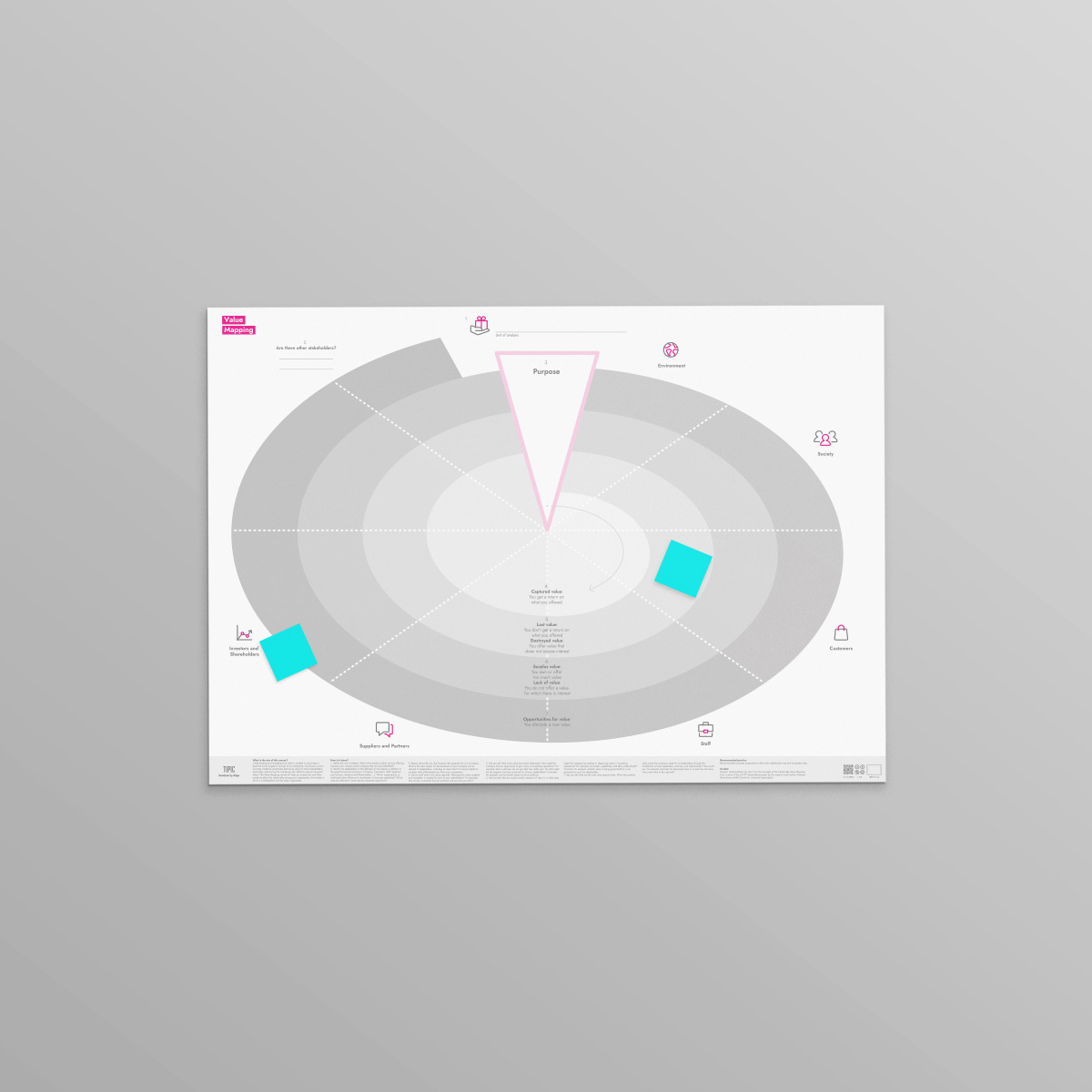
Understanding and managing how value is created in a business is essential to the long-term success of any enterprise. Could your current business model be proactively destroying value for other stakeholders, potentially undermining the company's own ability to capture long-term value? The Value Mapping canvas will help you answer this and other questions about the relationship among your organization, the context in which it is embedded, and the value it generates.
Is your company making the most of the value from the value you create for your customers and other stakeholders?
How to use the Value Mapping
1. First Step
Define the unit of analysis. What is the product and/or service offering, business unit, industry sector company that you have identified?
2. Second Step
Identify the stakeholders of the defined unit of analysis in addition to the essential ones (Environment, Company, Customers, Staff, Suppliers and Partners, Investors and Shareholders, ...). Which organizations or individuals have influence or involvement in business operations? Which are affected in some way by corporate operations? Consider who is involved in the value creation network and the external impacts of your business activities.
3. Third Step
Think about the aim, the Purpose, that supports the unit of analysis. What is the main reason for the existence of your company and its network of stakeholders, including its value chain? It may be helpful to consider what differentiates you from your competitors.
4. Fourth Step
Ask yourself what is the value captured. What positive value, tangible and intangible, is created for each of your stakeholders? For example, why do your customers buy the products and services you offer?
5. Fifth Step
Ask yourself what is the value lost and/or destroyed. How might the company miss an opportunity to gain value in its existing operations? For example, when customers do not get what they really want. Or what might be the negative business outcomes for all your stakeholders? Consider, for example, environmental impacts such as pollution.
6. Sixth Step
Ask yourself what the surplus and/or absence of value is. In what ways might the company be wasting or dissipating value in its existing operations? For example, are assets, capabilities, and skills underutilized? Consider, for example, whether value is being generated but is not perceived as such by stakeholders.
7. Seventh Step
Ask yourself what are the new value opportunities. What new positive value could the company create for its stakeholders through the introduction of new capabilities, activities,